In recent years, Sub-Saharan Africa has faced major grid instability with frequent planned and unplanned power cuts, as well as rising electricity prices, which have caused disruptions to daily life and the economy. In response, the government is accelerating the transition to new energy sources, especially renewables, by investing heavily and involving more private players, while also involving the commercial and industrial (C&I) sectors in power generation. Meanwhile, the continent’s strong solar potential and the drop in solar and battery storage costs (driven in part by lower lithium carbonate prices) are making solar-plus-storage an increasingly attractive investment rather than an optional add-on.
However, battery storage is a complicated technology, and there are two main criteria that C&I and Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) stakeholders are typically concerned about.
Battery Safety and Efficiency: The Key Concerns
A survey by TÜV Rheinland revealed that safety issues were the biggest concern among the constraints for the development of energy storage systems (ESS).
Unlike utility-scale ESS, C&I projects pose a greater safety risk, as they are usually installed in densely populated areas with higher population density and in the vicinity of valuable assets such as machinery, server rooms, combustible materials, etc.
Huawei recognizes the importance of both safety and efficiency, and has worked uncompromisingly to achieve some of the highest levels of safety and efficiency in its energy storage systems.
Safety With the Huawei Grid-Forming ESS
Safety has always been a cornerstone of Huawei’s product design, evident in its energy storage systems. Huawei takes pride in establishing safety requirements that are more stringent than the existing industry standards.
Instead of incorporating one or two common safety features, Huawei’s ESS features a holistic cell to consumption (C2C) safety design, making the system safe for use from its smallest unit all the way to its entirety. Additionally, the C2C system boasts a dual architecture, focusing on both electrical and thermal link safety.
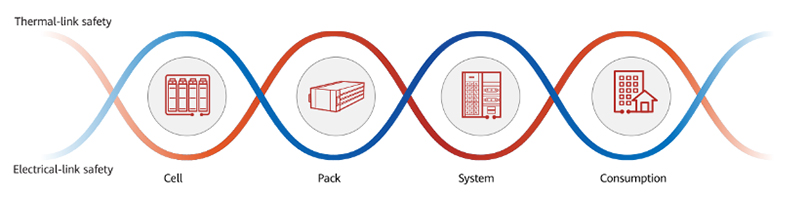
Huawei grid-forming ESS C2C dual link safety architecture
Let us examine how Huawei achieves maximum safety at each level through both electrical and thermal links.
Electrical link
The biggest risk to an energy storage system, electrically caused, is short circuits. Nearly all fires related to electrical components can be attributed to short circuits, making it an extremely crucial risk to address. Huawei does this by implementing an advanced short circuit prevention and isolation system in its ESS.
Cell level: At the cell level, Huawei uses a dual intelligent detection system, which can detect 13 types of cell faults and effectively prevent most short circuits.
Pack level: At the pack level, the greatest risk leading to short circuits is poor or rapidly degrading insulation. Huawei’s ESS uses a six-sided insulation that isolates all components, significantly reducing the risk of contact between isolated parts and reducing the risk of short circuits.
System level: When it comes to the entire system, most ESS adopt a four-layer protection, which leaves a blind spot, typically at the rack level contactors. Huawei’s five-layer protection enhances safety by eliminating this blind spot. Another noteworthy thing is the system’s rapid shutdown time. While most conventional energy storage systems have a shutdown time of over a second, Huawei’s ESS can shut down within an impressive 5 milliseconds when it detects a short circuit.
Consumption level: Finally, at the consumption level, Huawei uses a 24-hour, triple RCD (residual current device) protection that detects current leakage, resulting in avoided short circuits as well as improved system health and reliability.
Thermal Link
The importance of thermal safety in an ESS cannot be overstated, which is why Huawei implements the same C2C safety system to prevent thermal runaway as well as suppress it rapidly:
Cell level: Huawei’s ESS uses a high-temperature-resistant silicone foam insulation around each battery cell, reducing the heat flow between cells. It also uses an advanced liquid cold plate that houses a dual-loop heat-dissipation design to dissipate cell heat in no time.
Pack level: The pack level safety is ensured by a positive-pressure oxygen blocking design, which stops external gases from entering the battery pack due to a pressure difference, effectively preventing oxygen from entering the battery pack and reducing the likelihood of fire in the battery pack.
System level: Huawei secures system level thermal safety through a design that minimizes the risk of cabinet explosion. It does this by using a directional gas exhaust, connecting the pressure relief valve at the rear of the battery pack to the duct at the rear to form an L-shaped directional duct. This prevents the accumulation of combustion gases inside the cabinet and greatly reduces the possibility of an explosion.
Consumption level: In the highly unlikely event that combustion gases do accumulate inside the cabinet, steadily raising pressure to the point of explosion, Huawei’s ESS prevents uncontrolled explosions by using a top explosion vent with ropes. In this case, only the top panel is subject to explosion and held in place by ropes, unlike conventional designs, where all parts of a cabinet undergo explosion, often resulting in risk of injury and cabinet disintegration.
TÜV Rheinland Recognises Huawei ESS’s Remarkable Safety
To ensure that its energy storage systems surpass even the strictest safety standards, Huawei not only designed a cutting-edge safety architecture but also tested it rigorously. It commissioned TÜV Rheinland, one of the foremost testing organizations, to test and certify its ESS for safety.
TÜV Rheinland put Huawei's ESS through rigorous testing, adhering to standards even more demanding than the current industry benchmarks. With over 100 cell components and 300 battery packs tested, the results showcased the outstanding safety features of Huawei's ESS. This thorough evaluation not only underscores the system’s reliability and performance but also earned it the world’s highest safety certification for ESS.

Huawei receives the world’s first highest-level safety certification from TÜV Rheinland
On November 17, 2025, Huawei Digital Power's C&I Hybrid Cooling Grid Forming ESS has successfully passed a stringent extreme ignition test witnessed by TÜV Rheinland. Conducted at a national key fire safety lab, the test is the industry's first fire assessment of an ESS in compliance with the latest UL 9540A:2025 standard. Its exceptionally rigorous conditions establish a new safety benchmark for the sector.
Extreme Challenge: Rigorous Test Environment
The test was designed to create the industry’s most demanding verification environment, evaluating the safety performance of ESSs under extreme ignition scenarios. A pack-level overcharge method was used to trigger simultaneous thermal runaway in 60 battery cells—simulating a "worst-case upon ignition" scenario. Compared with tests involving only single or a few cells, the severity of this assessment increases exponentially.
Test data robustly validates the safety and reliability of Huawei's C&I GFM ESS. When the fire temperature reached 961 ℃, the highest cell temperature of an adjacent ESS was only 45.3 ℃, well below the threshold for opening the cell explosion-proof valve. The system fully complied with UL 9540A:2025 requirements, with no fire propagation between units.
The recorded peak heat release rate (HRR) was 3 MW. Total combustion lasted less than three hours before self-extinguishing. Under open-door burning conditions, the system rapidly managed heat release, demonstrating superior thermal management capability.
Efficiency of the Huawei Grid-Forming ESS
The second most important factor C&I customers focus on is efficiency. An energy storage system’s efficiency dictates how much power is utilized and how much is lost in conversion losses during charging and discharging. The better a system’s efficiency, the higher its return on investment (ROI). Although battery technology has advanced rapidly to become more efficient than ever, different battery brands can have noticeably different round-trip efficiencies (RTE).
Let us now move on to the next critical aspect of an ESS – efficiency, and see how Huawei excels at it.
Unsurprisingly, a lot of the things that make Huawei’s ESS extremely safe are also the same things that make its battery highly efficient. For instance, the hybrid cooling technology upgrades conventional thermal management from a single-mode regime to an adaptive multimode control strategy. In simple terms, the thermal management involves a scenario-based, environment-aware cooling that cuts auxiliary power consumption by 30%, boosting the system’s efficiency.
Thermal management is the crucial link between safety and efficiency. A properly designed thermal management system creates both a safe and efficient system. Huawei uses a wind-liquid smart cooling architecture, which combines the advantages of both air-cooled and liquid-cooled systems to maximise efficiency.
Huawei’s claims are supported by independent verification. Recently, Huawei commissioned the University of Pretoria for the proof of concept (POC) testing of Huawei Digital Power’s 215 kWh C&I storage system. The University of Pretoria, with over a century of esteemed history, is one of the most respected public research institutions in Africa.
Upon testing, it was confirmed that Huawei’s ESS has a striking round-trip efficiency (RTE) of 91.3%. This means that less than a tenth of the energy is lost in charging-discharging and the related DC-AC conversions.
Final Thoughts
Huawei is dedicated to improving the safety and efficiency of energy storage solutions, which is particularly important for Sub-Saharan Africa. By providing safer and more efficient energy storage solutions, Huawei plays a crucial role in helping the region’s transition to a new energy system.


